MgO Ceramic Substrate Manufacturing Technology
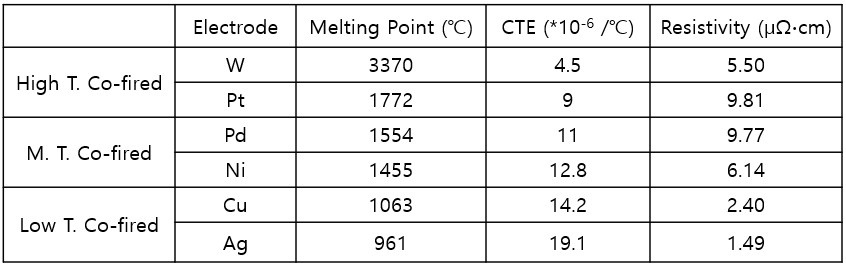
표 1. 동시소성 전극 특성
[산화마그네슘 세라믹 기판 제조기술]*
세라믹 기판은 전자회로 기판, LED 방열기판 등에 주로 사용되며, 최근 전자회로의 집적도가 증가하면서 배선의 고밀도와 다층 집적화로 급속히 변화하고 있어 전극과 동시소성이 가능한 적층세라믹 기판용 소재가 크게 요구되고 있다.
적층세라믹 기판소재는 사용전극과 (1) 우수한 동시소결 특성, (2) 유사한 열팽창계수, (3) 내구성을 위한 적당한 휨강도, (4) 전극과의 우수한 접합성, (5) 저가격이 요구되며, 현재, 표 1에서 보는 바와 같이 고온소성(1500 ∼ 1600℃)용으로 알루미나(Al2O3) 로 조성된 기판재료와 저온소성(850 ∼ 925℃)용으로는 유리/세라믹 복합재료가 주로 사용되고 있다. 그러나, 고온 동시 소성는 소결성, 기계적 강도, 전극 접합성 및 열전도성 면에서는 우수하나 고가의 전극과 높은 소성온도로 인한 생산수율과 단가가 큰 문제이며, 유리/세라믹의 경우는 다량 함유된 유리로 인한 일부 특성 저하가 있다.
이러한 특성의 개선을 목적으로 많은 연구가 진행되고 있으나 부분적인 개선이 이루어질 뿐이며, 근본적인 해결방안이 도출되지 못하는 실정으로 적층세라믹 기판이 고집적화하는 추세속에 신뢰성을 확보하고 효율적인 생산을 위해서는 상기에서 설명한 요구조건을 만족할 수 있는 새로운 형태의 중온 동시소성용 세라믹 기판 조성물의 개발이 절실히 요구되고 있다.
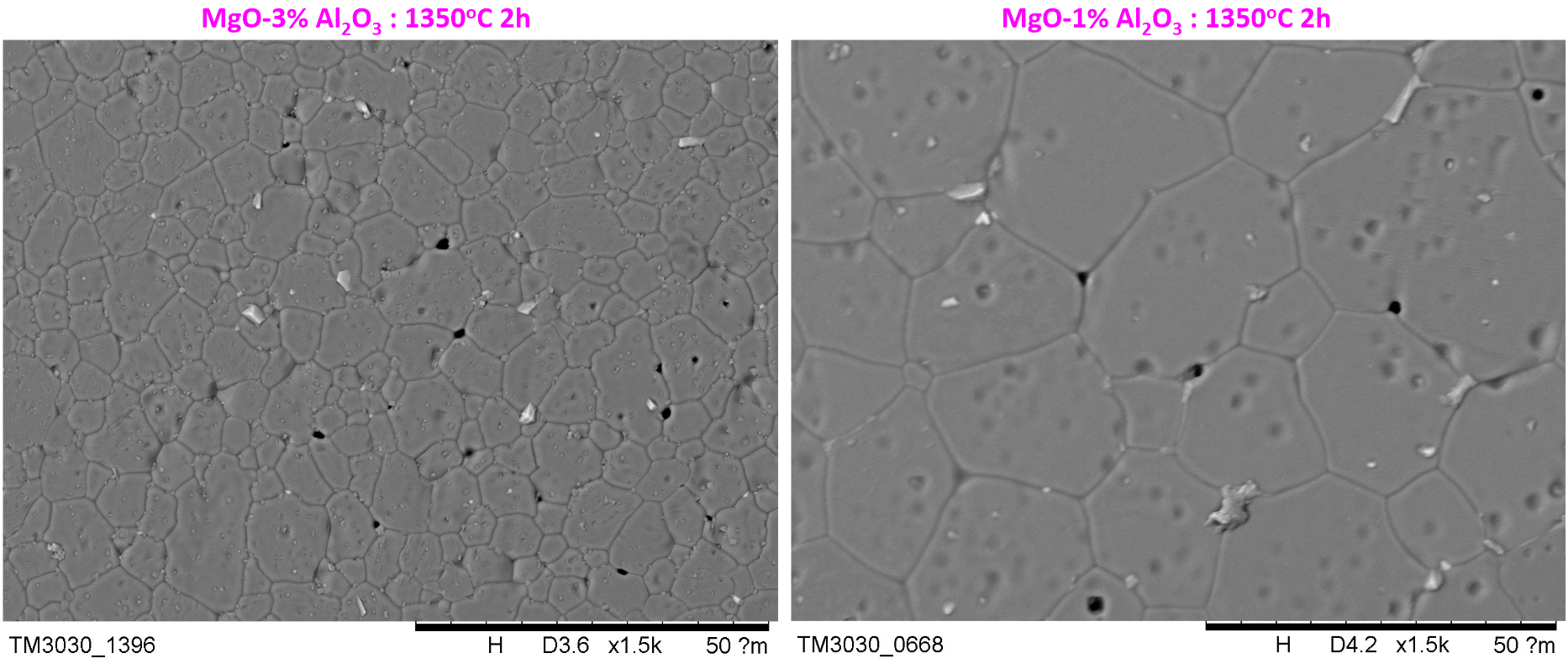
저가이고 전기 전도성이 양호한 Ni 전극과 열팽창계수가 비슷하고 열전도도가 높은 마그네시아(MgO)의 소결특성을 개선시킨 중온 동시소성용 마그네시아 세라믹 기판 조성물을 개발하였다. 본 기술은 적층 세라믹 기판을 제조함에 있어 가격이 저렴한 Ni 전극과 동시소성이 가능하도록 1400℃ 이하에서 소결특성과 Ni 전극과의 접합성이 우수한 중온 동시소성용 마그네시아 세라믹 기판 제조가 가능하다. 뿐만 아니라 소결 첨가제 조절을 통해 1000℃ 에서도 소성가능하게 만들 수 있는 장점이 있다.
*) Kor. Patent Pending
[Magnesium Oxide Ceramic Substrate Manufacturing Technology]*
Ceramic substrates are mainly used for electronic circuit boards, LED heat dissipation substrates, etc., and as the integration of electronic circuits has increased recently, there has been a rapid change to high-density wiring and multi-layer integration, and thus, there is a great demand for materials for laminated ceramic substrates that can be simultaneously fired with electrodes.
Laminated ceramic substrate materials require (1) excellent simultaneous sintering characteristics, (2) similar thermal expansion coefficients, (3) appropriate flexural strength for durability, (4) excellent bonding properties with electrodes, and (5) low price. Currently, as shown in Table 1, substrate materials composed of alumina (Al2O3) for high-temperature firing (1500–1600°C) and glass/ceramic composite materials for low-temperature firing (850–925°C) are mainly used.
However, although high-temperature co-firing is excellent in terms of sinterability, mechanical strength, electrode bonding, and thermal conductivity, the production yield and unit price due to the expensive electrode and high sintering temperature are major problems, and in the case of glass/ceramics, the material price is high due to the large amount of glass contained, and various characteristics are also unsatisfactory.
Although many studies are being conducted for the purpose of improving these characteristics, only partial improvements have been made, and fundamental solutions have not been derived. Therefore, in order to secure reliability and produce efficiently in the trend of high integration of multilayer ceramic substrates, the development of a new type of medium-temperature co-firing ceramic substrate composition that can satisfy the requirements described above is urgently required.
A medium-temperature co-firing magnesia ceramic substrate composition that improves the sintering characteristics of a low-cost, good electrically conductive Ni electrode and magnesia (MgO) with a similar thermal expansion coefficient and high thermal conductivity was developed. This technology enables the production of a magnesia ceramic substrate for medium-temperature co-firing with an inexpensive Ni electrode at temperatures below 1400°C, which has excellent sintering characteristics and bonding properties with Ni electrodes, enabling co-firing with an inexpensive Ni electrode when manufacturing a laminated ceramic substrate.
